Saturday, 21 December 2013
Tuesday, 13 August 2013
Hello, this little post will explain in rough details how you start hacking a specific target.
First. There are many different ways going about this, but this is one way.
Information gathering
The first thing you want to do when targeting a specific target is get
as much information as possible before a front attack(if any, being
quiet is much better)
Now this step can take ages if you really want
a detailed level of knowledge. And if you are serious about hacking
your target, you should be detailed here.
What sort of information
do I look for you might ask yourself? Well, anything really. Anything
surrounding the target and even things that surround things that
surround your target. Here is a short list of things that might be
useful;
IP(s), some machines/domains/systems or whatever have multiple domains
ISP(s), if small ISP(s), get owner details here as below
Owner. Email, name, location, family, hobby's, Facebook account, phone number
*Open ports. On ALL of the ips/servers if there are multiple
Service signatures, find out as much as possible about all the open
ports, are they in use? What software are they running at the other end?
Do the services reveal any other information about the system? OS?
Internal IPS?
Hosters(In most cases there will be a hosting company)
Hosters information - Owner and all of that(If the company is small)
Hosters member system, how does the members login? Is there a login? Is
there a forgot password function? Can you exploit the hoster
instead?(might be easier in some cases)
DNS records(if any), subdomains? Hidden domains/info? DNS hosters? Same as above.
The physical server(s) location / datacenter
And the list goes on and on and on. Literally EVERYTHING about the
company/system/server/target are relevant. The more info you got, the
easier it will be attacking him/her/them/it.
You should decide
if you want to target the system or the people of your target. That is,
code/system flaws or human flaws(keyloggers, Trojans, social
engineering, info gathering + password guessing, etc). This decision
should depend on the information you find about your target. Both can be
tried ofcourse, just make sure the target does not know you are trying
to hack it, often one of the attempts will set off alerts.
This
whole information gathering part might seem unnecessary, but really.
Its neat, lets you put things in perspective so you can find the best
point of entry.
The attack
Before an attack is lunched, there are a few things you need to think about. Here is a list of things you should think about;
Will this company/target rage crazy if I hack them? If so, check 3rd point.
Will police or other agencies be contacted if I hack them? If so, check 3rd point.
*Is my privacy good enough? Are you behind a proxy(s)? Should you? Do the proxy log?(It shouldn't)
Are they running any services at all? If not, you don't really have any virtual way in..
Are they running web applications? These are typically easier to hack
than services. And have a higher percentage rate of flaws.
Do the target got a open router/switch/modem system? This often happens with home computers/networks.
Are your target running platforms with logins? These could be targeted.
Do you have enough time? Its a good practice to have time enough to do
the entire attack in one go. Else you might fire off warnings for the
target, and he can go into a bombshelter We don't want that now, do we?
Now there are tree ways of attacking in this guide.
- Service/software exploitation
- Web application exploitation
- Human factor exploitation
Service/software exploitation
Here you will exploit one or more services/programs running on the
target system. In most cases, this will be called bufferoverflow. This
can do everything from bypassing a login to give you instant shell
access. In scenarios where the target is running services which is not a
web server(can be tho) this might be the way to go.
Web application exploitation
This is without a doubt the most vulnerable field. Web applications are
flawfull, 70% or so of all pages got some sort of web application flaw,
this ofc may vary from an stupid XSS to a serious RFI. In scenarios
where the target system are running a web server, this is the first
thing to check. Do always check web applications before going on to
service exploitation if you just want to get the target hacked.
Human factor exploitation
Now if all other things fail, there is ALWAYS a human factor. This can
be social engineering the target to give you limited access, and you
work your way up from there. Or simply tricking the target to trust you
and in some strange way share his password, perhaps not for the system
you are targeting, but for his email or an online account or whatever,
stupid people tend to use the same password or the same password syntax
everywhere. Keep in mind that the human factor doesn't necessarily have
to be your targets owner, could be the hoster, the DNS hoster, the ISP,
family.
Finale note
If you think its necessary, clear your
tracks. If you ask me, if you can see that you have been there you
didn't do it right. Take care, be safe.
Sunday, 11 August 2013
Zorin OS 6.2 lite has been Released
Zorin OS Lite 6.2 is built on the Linux architecture so it is completely open source and it's based on Ubuntu, one of the most used Linux operating system in the world.
This latest version of Zorin OS Lite is still based on Lubuntu 12.04.2 (Precise Pangolin), which was released only a couple of days ago, and it uses the LXDE desktop environment.
Zorin Look Changer, Zorin Internet Browser Manager, Zorin OS Lite Extra Software and other programs from earlier versions have been added to Zorin OS 6.2 Lite.
Download (MD5) from here: zorin-os-6.2-lite.iso (650MB)
Another Great Ubuntu Flavor Linux Lite 1.0.6 (Based on Ubuntu 12.04)
It is also recommended to those people who are new to Linux or for those who want really lightweight desktop environment. It is also great choice for old laptop or desktop you gave up on a few years back. Linux Lite is a showcase for just how easy it can be to use Linux. From familiar software like Firefox and Thunderbird, to simply named menu items, to one click updates and software installs.
Linux Lite team just released 1.0.6 version for 32bit and 64bit with Xfce desktop environment, based on Ubuntu 12.04.
Linux Lite 1.0.6 new features include easier networking setup between Linux Lite and Windows or other Linux operating systems, a system report tool to help troubleshoot problems, support for scanners, Bluetooth and a brand-new login screen. The Help and Support Manual is our most comprehensive to date and is available both offline and online.
Changelog:
- Firefox 21.0
- Kernel 3.2.0.40 pae
- Rewrote Help & Support Manual
- Added Scanner support.
- Added Bluetooth.
- Added 'Drives' shortcut to home folder.
- Added Show Desktop button.
- Added support for iDevices.
- Added right click 'Open as Administrator' to Thunar.
- Added/Removed Install Additional Software scripts.
- Added Enable/Disable automatic login to System menu.
- Added Network Share Settings to System menu.
- Added Create System Report to System menu.
- Replaced Wicd with Network Manager.
- New live boot menu.
- New login screen.
- New install slides.
- Announcement of the Linux Lite Shop.
- Fixed auto login if chosen during installation.
- Bug fixes.
- and So on...
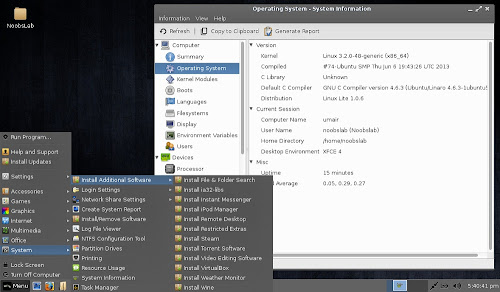
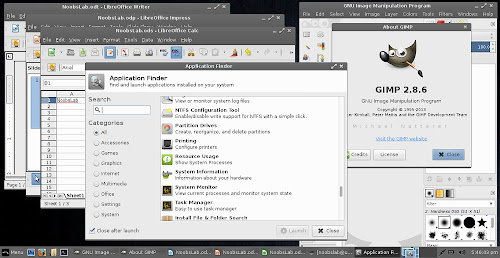
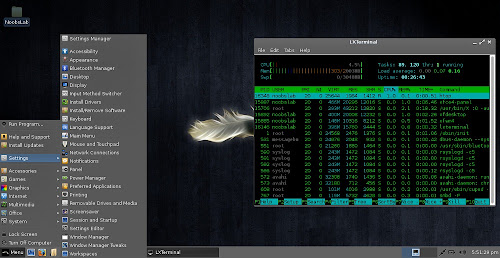
Screenshots
Boot Screen
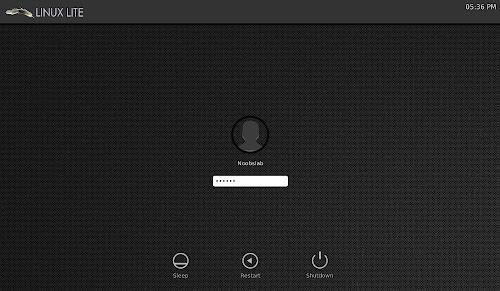
Login Screen
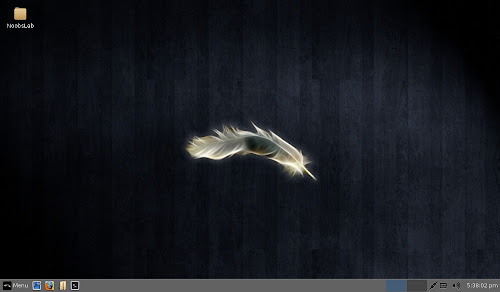
Desktop
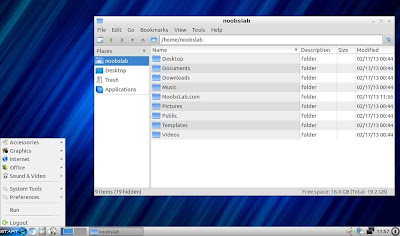
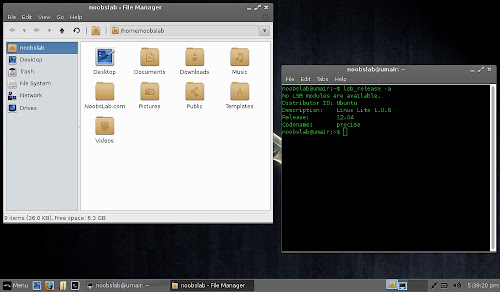
File Manager & Terminal
Additional Software & System Info Tool
Installed Applications & Application finder
Task Manager
Yahoo Messenger is one of the highly
popular and most widely used instant messaging service in the world
offering a wide variety of features to its users, all for free. This has
made it the right choice for all those who are waiting to chat and
communicate with their far away friends and relatives.
However, while some people use Yahoo
Messenger only to chat with their friends and known ones, many others
use it to have fun by joining the chat rooms and chatting with the
strangers. If you’re a similar person who would like to have fun during
the chat, this post if for you!
In this post, I will show you some really interesting Yahoo Messenger hacks
using which it is possible to play pranks with your friends and
strangers during the chat. Below is a list of some cool hacks that
you’re sure to enjoy:
1. Chat with Multiple Names Simultaneously
How about chatting with your friend with
two or more different names at a time? Well, do not think that this is
impossible! This can easily be done with a simple workaround which
enables you to chat with as many different names as you can with the
same or different people.
For example, you may chat with Person-A using one name and with Person-B
using the other. You can also chat with the same person using different
names or any other combination. All of this goes really unnoticed by
the user on the other side, while you are sure to have some real fun.
Here is a step-by-step procedure to implement this hack:
-
Sign in to your Yahoo Messenger. From the top, click on Messenger -> My Account Info. You will be taken to a web page where you need to log in to your account.
-
Now, you should be on the Profile Settings page. Scroll down to see the option Account Settings as shown below. From there, click on the link which says: “Manage your Yahoo! aliases”.

-
From the Aliases page, click on: “Add an alias”. You can create as many aliases you want. Choose unique names for your alias and once you’re done, click on “close”.
- You need to sign out of Yahoo Messenger and sign in
again to see the changes. Once you have done this, double-click on any
name from your contact list or chat room to open a new chat window. You
should now see a list of your aliases appearing in the chat window to
choose from.

-
To chat with multiple names with a single person, just follow the steps below:
-
Double-click on the name of the person in the chat room or contact list.
-
Select any name from your “alias” list and ping the user with that name. Immediately close the chat window before you get a reply from that person.
-
Again double-click on the same person’s name and ping him/her with another name from your “alias” list. This time do not close the window.
-
Just wait a few seconds! When the person replies to both your pings, you will have two tabs in the same chat window from where you can chat with the same person using two different names. Enjoy!!!
-
How to Know if Someone Accessed My Computer When I am Away
Do you have a feeling that someone tried to access your computer
when you stepped out for a lunch or quick coffee break? Perhaps
your colleague or the person sitting in the next desk tried to log in or
play something wicked on your computer while you were away for a quick
session.
So, how do you know if someone tried to
access your computer in your absence? Well, here is a way by which you
get notified every time when such an attempt is made.

The website called MouseLock.co
gives a solution here. All you have to do is visit the site’s homepage,
sign in to your Gmail account and select your secret point (unlock
code) from the screen. Once you do this, you will have to place your
mouse cursor into the slot shown and click on it. This will activate the
mouse lock feature on your computer screen.

So, when an unauthorized person tries to
move the mouse in your absence, he will be given just a few seconds to
select the unlock code. Upon failure to do so, you will get an instant
notification about the intrusion in your mailbox.

If you have a webcam attached to your
computer, you can even get the photo of the person trying to intrude.
This will make it easy for you to figure out who actually was the
person.
As this is an easy to use web
application, you can use it any time just by loading the MouseLock
website without the need to install anything on your computer. Even
though MouseLock does not manage to prevent the intrusion, it will give
you an instant notification about it, so that you aware of what is
happening at your desk when you are away.
How it Works?
MouseLock operates by using the
“mouseLeaveEvent” from JQuery to track the mouse movements. On the other
hand, it uses the “getUserMedia()” API that is supported by Chrome and
Firefox to capture the webcam photographs.
Monday, 5 August 2013
Monday, 22 April 2013

Ettercap is by far one of the most powerful Security Tools to perform Communication Interception on both Local and Wireless Networks.
A few days ago, Version 0.7.5 was released, introducing three new and exciting features:
1. SSL Password Interception. Captures user credentials from secure web portals such as Facebook, Yahoo, Hotmail and Gmail. This technique is based on the "Sslstrip" tool.
2. IPv6 Support. With this feature, we can now perform security tests over this network generation, giving us new and exciting Ethical Hacking opportunities.
3. NBNS Spoofing. Steals the identitiy of any network device or service, as long as it is based on Netbios name resolution. This attack is very useful on Windows Networks and Samba servers. It can also be used to attack other technologies such as SAN and NAS.
As Security Experts, we need to stay at the cutting edge of our field, testing new attack tools and their capabilities as soon as they become available.
Unfortunately, Ettercap's installation procedure is very poorly documented. Despite my amazing Google Powers, I have not found any useful Internet tutorial. To make things worse, even the great BackTrack distribution does not include the new version.
Furthermore, I really doubt we'll see the new version on Ubuntu's software repositories any time soon. Ettercap authors strongly recommend using "development" libraries, which are considered "unstable" for most production environments.
To solve the conundrum, I decided to write this tutorial, explaining a detailed installation procedure for Ettercap on Ubuntu 12.04. Of course, a rookie Hacker might say "I'll just install it on Windows! Problem solved!".
Well, if you are one of these rookies, I have bad news for you. Installing it on Windows is extremely easy. However, this platform does not support the new SSL attack!
So, with this Tutorial, I'm going to help you become one of the first Ethical Hackers in the whole Universe with the knowledge and power to use the new Ettercap awesome features.
INSTALLATION PROCEDURE
1. Installing Dependencies. Ettercap requires a lot of software libraries not usually available on a standard Ubuntu system. To install them, just open a terminal and run the following commands:
apt-get install -y cmake cmake-curses-gui
apt-get install -y libgtk2.0-dev libnet1-dev flex build-essential
apt-get install -y linux-headers-`uname -r` libpcre3-dev libpcap0.8-dev openssl
apt-get install -y libssl-dev ncurses-bin libncurses5-dev libnet6-1.3-dev libpthread-stubs0-dev
apt-get install -y zlib1g-dev libltdl-dev pango-graphite pkg-config libpango1.0-dev
apt-get install -y libatk1.0-dev libgtk2.0-dev autoconf byacc
(To accelerate the installation, open this tutorial in your browser and just copy-paste the instructions on your terminal, instead of entering them manually).
2. Sslstrip support. This new feature requires a recent libcurl library version, not yet available in Ubuntu's repositories. So, we need to install it from source. Run the following commands:
cd /usr/src
wget http://curl.haxx.se/download/curl-7.28.0.tar.gz
tar xvfz curl-7.28.0.tar.gz
cd curl-7.28.0
./configure
make
make install
In this tutorial, I'm using /usr/src as destination folder, feel free to use whatever you want.
To make sure Ettercap finds the new library, open the /etc/ld.so.conf file. Add /usr/local/lib at the end. Save the file and run ldconfig to complete the installation.
2. IPv6 Support. This new feature requires a recent libnet library version, not yet available in Ubuntu's repositories. Again, we are going to install it from source. Go to http://sourceforge.net/projects/libnet-dev/ and download the libnet-1.1.6.tar.gz file to any folder. In this tutorial, I'm using /usr/src
Run the following commands from your terminal:
cd /usr/src
tar xvfz libnet-1.1.6.tar.gz
cd libnet-1.1.6
./configure
make
make install
ldconfig
3. Ettercap Installation. Open http://sourceforge.net/projects/ettercap in your browser. Download ettercap-0-7.5.tar.gz to any folder.
In this tutorial, I use /hack/network/mitm (I install all my "Man in The Middle" attack tools in this folder, hence the name. Of course, you can choose any other folder).
Run the following commands in your terminal:
cd /hack/network/mitm
tar xvfz ettercap-0.7.5.tar.gz
cd ettercap-0.7.5
mkdir build
cd build
cmake ..
ccmake ..
You'll see the following screen:

Change the following fields, with the indicated values:
ENABLE_IPV6 ON
FOUND_LIBCURL /usr/local/lib/libcurl.so
HAVE_LIBNET /usr/local/lib/libnet.so
Press Enter after modifying each field, press "c" to return to configuration mode, and finally "g" to save the changes and exit. Finish Ettercap's installation by running the following commands:
make
make install
SSLSTRIP CONFIGURATION
1. Sslstrip capability requires root privileges to make some temporal changes to the local firewall. To grant them, open Ettercap's configuration file /etc/ettercap/etter.conf. Modify the text at line 17, so it reads ec_uid = 0.

2. Delete the # comment character from lines 171 and 172. These are firewall modifications required by Sslstrip, used only while Ettercap is running. Don't worry, they are just network traffic redirection instructions and do not jeopardize your firewall integrity in any way.

Save the etter.conf file.
ETTERCAP TESTING
Run the following command:
ettercap -G
If everything works as expected, you'll see the following screen:

Congratulations! You are now one of the first and proud Ethical Hackers in the whole Universe to test the new and powerful Ettercap!
Now go have a drink... You know you deserve it.
Thursday, 4 April 2013
Itz COST Free but not EFFORT Free ;)
Now u can get your free domain name at
www.freedomainfactory.com
OR
www.freepremiumdomain.com
All u have to do is Sign Up....invite your friends thru your referal link and complete surveys to earn points..DATZ IT!!
Wednesday, 3 April 2013
Common Problem
(Still No Error in order by 10000--)
First thing you do when a website is vulnerable to SQL injection is to check
the number of columns inside the database.
Already tried to put 10000 columns test but still got no errors?
Having problems knowing the number of columns inside the database?
The reason is it is blocked by the WAF, but here is a method to bypass it.
Example Vuln:
http://
Example:
http://
If there is no error with that number of columns, it will be impossible for a small site like this. :)
To bypass this, you have to add ' after parameter id and also put + at the end.
So you will have something like this.. :)
http://
NOTE
YOU STILL HAVE TO CONTINUE USING THE ' AND + AS YOU CONTINUE LIKE THIS.
http://
HOPE YOU ENJOY THE TUTORIAL!
(Still No Error in order by 10000--)
First thing you do when a website is vulnerable to SQL injection is to check
the number of columns inside the database.
Already tried to put 10000 columns test but still got no errors?
Having problems knowing the number of columns inside the database?
The reason is it is blocked by the WAF, but here is a method to bypass it.
Example Vuln:
http://
Example:
http://
If there is no error with that number of columns, it will be impossible for a small site like this. :)
To bypass this, you have to add ' after parameter id and also put + at the end.
So you will have something like this.. :)
http://
NOTE
YOU STILL HAVE TO CONTINUE USING THE ' AND + AS YOU CONTINUE LIKE THIS.
http://
HOPE YOU ENJOY THE TUTORIAL!
How to Become a Hacker:
1. Learn TCP/IP, Basic
Information gathering,
Proxies, Socks, SSL, VPN, VPS,RDP, FTP, POP3, SMTP, Telnet,
SSH. 2. Learn Linux, Unix, Windows
- You can do this using
vmware or any virtual
desktop utility. 3. Learn a programming
language that's compatible
with all OS - Perl, Python, C . 4. Learn HTML, PHP, Javascript,
ASP, XML, SQL, XSS, SQLI, RFI,
LFI 5. Learn Reverse engineering
and crack some programs for
serials easy ones like mirc,
winzip, winrar or old games. 6. Code a fuzzer for common
protocols - ftp, pop3, 80, 8080 -
Pick some free software like
ftp server, mail server, apache
or iis webserver or a
webserver all-in-one pack, or teamspeak, ventrilo, mumble. 7. Code a tool that uses grep to
sort out unique code in source
codes. 8. Make a custom IPtable, IPsec
firewall that blocks all
incoming traffic and out going
traffic and add filters to accept
certain ports that your
software or scripts use. 9. Pick a kernel in linux or
unix, also pick a Microsoft OS
version lets say Winxp pro sp2
put them on the virtual
desktops (vmware) and find
and code a new local exploit in those versions, then install a
Apache webserver on the
Linux/Unix and a IIS
webserver on the winxp pro
and attempt to find and code a
new local reverse_tcp_shell exploit. 10. Learn Cisco Router and
Switch configuration and
setup. 11. Learn Checkpoint Setup and
Config 12. Learn Wifi scanning,
cracking, sniffing. 13. Pick a person in you
phonebook for the area code
you live in or city then ring
the person on a anonymous
line like skype or a payphone
or a carded sim and attempt to social engineer the person for
his name, address, data of
birth, city born, country born,
ISP connected with, Phone
company connected with,
What bank he/she uses and anything else you can get.
Then Attempt to ring using a
spoof caller ID software with
the person's phone number -
call the ISP and try reset the
password to his/her internet connection/ webmail, get
access to bank account or ask
them to send out a new *** to
a new address (drop) with a
new pin, reset of phone
company passwords. 14. Use your information
gathering skills to get all the
information off a website like
a shop then use the spoof
callerID software or hack your
phone to show a new number of the Webserver's Tech
Support number then ring the
shop owner and try get the
shop site password. 15. Do the same thing but
attempt to use a web attack
against a site or shop to gain
admin access. 16. Once got access upload a
shell and attempt to exploit
the server to gain root using a
exploit you coded not
someone else s exploit. 17. Make your own Linux
Distro 18. Use your own Linux Distro
or use a vanilla Linux gnome
(not kde) keep it with not
much graphics so you can learn
how to depend on the
terminal and start from scratch install applications that you
will only need for a blackbox
(Security test box), make
folders for fuzzers, exploits,
scanners..etc Then load them
up with your own scripts and other tools ( By this stage you
shouldn't need to depend on
other peoples scripts). 19. Learn macosx and attempt
to gain access to a Macosx box
whether it be your own or
someones else s. 20. Create a secure home
network and secure your own
systems with your own
Security policies and firewall
settings. All this isn't a over night
learning it will take a nice 3 - 4
years to learn a bit of this 5+
years to learn most of it and
even then you may need time
to keep learn as IT keeps changing everyday.
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)